What is a Tibial Eminence (Tibial Spine) Fracture?
Also called the tibial spine, the tibial eminence is the attachment site of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee. This bony attachment at the top of the tibia (shin bone) can fracture or break if a child falls from a bicycle or is injured while playing sports. Tibial eminence fractures can involve the tibial plateau (top of the shinbone) and range from very small fractures to large fractures which involve a significant amount of damage. Dr. Armando Vidal, pediatric sports medicine and orthopedic surgeon treats children and teens in Vail, Aspen and the surrounding Denver, Colorado communities who have experienced a tibial eminence fracture.
Who is at risk for a tibial eminence fracture?
This condition occurs most often in children between the ages of 8 and 14. These fractures account for 2% – 5% of knee injuries in the pediatric population.
Why aren’t adults at risk for a tibial spine fracture?
During the final stages of bone growth (usually between the ages of 14 and 16) the chondroepiphyseal (growth plate) junction hardens and fuses at the site of the ACL tibial insertion. Once this occurs, it is very difficult (yet not impossible) to pull the ACL off of the tibia, breaking the tibial eminence. Only extreme trauma can cause the rare occurrence of a tibial spine fracture in skeletally mature adults and usually include additional injuries such as bone contusions, tearing of the MCL, PCL and meniscus. Dr. Vidal has seen this after high speed motor vehicle collisions, severe hyperextension or extreme skiing accidents.
How do you fracture the tibial spine?
In the pediatric population, fractures are most likely to occur while children are participating in sports activities such as:
- Falling from a bike (most common)
- Skiing
- Hyper-extension in sports like gymnastics
- Football tackle
What are the symptoms of a tibial eminence fracture?
A patient with a tibial eminence fracture usually complains of knee pain. Other symptoms include:
- Decreased range of motion
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected knee
- Rapid onset of swelling, heat, stiffness and pain (known as hemarthrosis – or bleeding within the joint.)
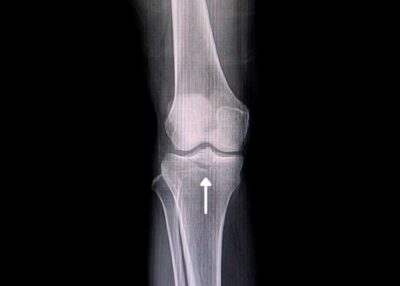
How is a fracture of the tibial spine diagnosed?
Dr. Vidal will take a thorough medical history of the patient and conduct a physical examination of the affected knee. Diagnostic tests such as an X-ray will show larger fractures of the tibia, however an MRI may also be needed to see small fractures and to assess any further knee damage.
How is a tibial eminence fracture repaired?
The goal of a tibial spine repair is to properly realign the bone back where it belongs (called an anatomic reduction). The method for this depends on the size and severity of the fracture.
- Small fractures that are still in the correct anatomical position can be treated with casting.
- Displaced fractures typically need to be arthroscopically repaired. This minimally invasive procedure would visualize and remove any barriers to reduction and the fracture would be fixed in place.
What are the goals of tibial eminence fracture surgery?
The tibial eminence contains the attachment site of the ACL and when it displaces, tension in the ACL is lost – therefore compromising its function. Additionally, the insertion site (anterior root) of the lateral meniscus is very close to the ACL tibial origin and is often also compromised with these fractures. Lastly, the extent of involvement of the fracture can vary quite a bit and often the articular surface (cartilage surface) of the tibia is involved as well. Addressing all aspects of this injury is the key to success.
The goals of surgery for tibial eminence fractures therefore are:
- Restore motion and eliminate the mechanical block that is created by the displaced piece of bone
- Restore the cartilage (articular) surface to its anatomic position to minimize the risk of arthritis.
- Restore meniscal root function and anatomy
- Restore ACL function and integrity
- Failing to address any of these components can result in clinical failure of the surgery and ultimately long-term joint dysfunction. Dr. Vidal has extensive experience with these injuries and has published the largest series in the literature on the outcomes of these injuries, their associated injury patterns and the risk of delayed ACL injury.
What are the risks of Tibial Eminence Fractures and Surgery?
- The greatest risk is a complication known as arthrofibrosis or scarring of the joint. This leads to stiffness and loss of motion. Oftentimes this requires a second surgery to remove scar tissue and manipulate the joint to regain motion
- Delayed ACL tear can occur after these injuries. In our data, this risk is almost 20% and is independent of whether or not the fracture was surgically repaired. The exact cause of this is unknown, but it probably related to intrinsic ACL injury that occurs with the injury itself and well as biomechanical factors that created the fracture initially.
- Symptomatic Hardware. Hardware is required to fix the eminence in position and can cause symptoms down the road that requires removal through a small surgical procedure.
What is the recovery time after a tibial eminence fracture repair?
In order for the patient to avoid arthrofibrosis (knee stiffness) in children with tibial eminence fractures, Dr. Vidal will have them moving the leg as quickly as possible. This may involve a CPM (continuous passive motion) machine to keep the knee moving. Early on, restricted weight bearing might be required as well until the fracture is sufficiently healed to tolerate weight bearing. Physical therapy and strengthening exercises will help return children in Vail, Aspen and the surrounding Denver, Colorado communities regain full motion and strength in the affected leg. Patients will usually return to their full level of activity in 3 to 4 months.
Pediatric Knee Surgeon
A tibial eminence fracture is an injury that occurs most commonly in young, active patients. In this injury, the top of the tibia, which acts as the attachment point for a ligament in the knee, fractures, causing instability in the knee. Pediatric knee surgeon, Doctor Armando Vidal provides diagnosis as well as careful surgical repair for young patients in Vail, Aspen, and the surrounding Denver, Colorado communities who have experienced a tibial eminence fracture. Contact Dr. Vidal’s team today!

Locations
180 S Frontage Rd W
Vail, CO 81657
226 Lusher Court
Ste 101
Frisco, CO 80443
322 Beard Creek Road
Edwards, CO 81632


